Interview Questions
1. Could you please provide an introduction about yourself? & Explain about your current project details and roles & responsibilities? video available
Hi, good morning Satish! My name is Sreenu, I am from Telangana. I have over 7 years of experience in the IT industry. Currently, I am employed at Persistence System. My current project name is SG Wealth. I've been involved in developing the User Registration Module within the banking domain.
For the implementation, we are using technologies such as Java, Spring, Spring Boot, Microservices, Spring Security, Spring Data JPA, and a MySQL database for the backend. On the frontend side, we are using HTML, CSS, Bootstrap, JavaScript, jQuery, and Angular.
These technologies were used to develop the application.
My Roles and Responsibilities:
1) Read FDD (Functional Design Document) and understand the requirement
2) If I have any questions about the requirement, note them down and ask the functional team in daily meetings
3) Design database tables
4) Prepare insert queries to insert data in static tables
5) Analyze components (classes and methods)
6) Create project for backend and implement code for backend (REST API)
7) Test the backend API using Swagger UI/POSTMAN
8) Write JUnit test cases for every individual API
9) Maintain the code coverage at a minimum of 95%
10) Push the code into the Git repository
11) Deploy the backend application in AWS cloud with the help of Jenkins tool
2. Explain about your current project architecture & request, response flow? video available
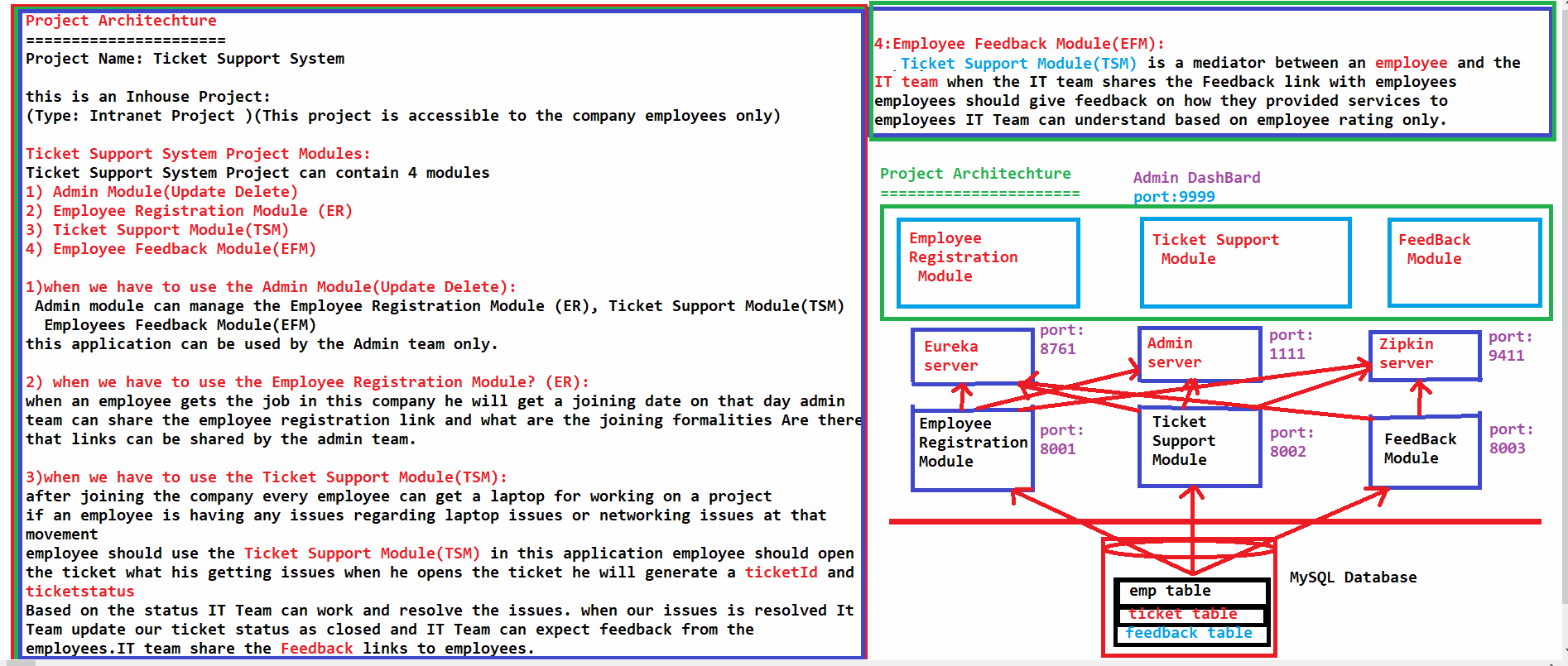

















3. Restful service http methods
GET retrieves data, POST creates new data, PUT updates existing data, DELETE removes data.
4. Handling exceptions in rest api using HttpStatus codes
Use HttpStatus codes like 400 for bad request, 404 for not found, and 500 for server errors to indicate specific error scenarios.
5. Spring boot data jpa types
Spring Boot supports various data types for JPA including String, Integer, Date, BigDecimal, and more for database mappings.
6. Can we save resource using PUT? Difference between PUT & POST?
PUT updates or creates a resource if it doesn't exist, while POST creates a new resource every time it's called.
7. What logging mechanism your using in current project?
We use SLF4J with Logback for logging, providing configurable and efficient logging capabilities.
8. What testing mechanism your using in current project?
We employ JUnit and Mockito for unit testing and integration testing to ensure robust code quality.
9. Have you use mocking framework?
Yes, we use Mockito for mocking dependencies in our unit tests, ensuring isolated and reliable testing.
10. What type of SDLC model your using in current project?
We follow Agile methodology, enabling iterative development and flexibility to adapt to changing requirements.
11. What project management tool your using in current project?
We use JIRA for project management, facilitating task tracking, issue management, and team collaboration.
12. What project build tool your using in current project?
We use Maven as our build tool to manage dependencies, build processes, and project lifecycle.
13. What project repository tool your using in current project?
We use Git with GitHub for version control and collaborative development, ensuring code integrity and team coordination.
14. What tool your using in current project to check code quality?
We use SonarQube to analyze code quality metrics, identify bugs, and ensure adherence to coding standards.
15. Have you involved in cloud deployment?
Yes, we deploy our applications on AWS, utilizing services like EC2, S3, and RDS for scalable and reliable cloud infrastructure.
16. Have you worked with tools like Docker, Jenkins?
Yes, we use Docker for containerization and Jenkins for continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD).
17. Java OOP concepts
Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) in Java includes concepts like encapsulation, inheritance, polymorphism, and abstraction to manage complexity and promote code reusability.
18. What is JDK and JVM
JDK (Java Development Kit) is a software development kit used to develop Java applications, while JVM (Java Virtual Machine) executes Java bytecode and provides runtime environment.
19. What is StringBuilder and StringBuffer
StringBuilder and StringBuffer are mutable sequences of characters in Java. StringBuffer is synchronized, whereas StringBuilder is not.
20. Is String Thread Safe
No, String objects are immutable and therefore thread-safe by default, but StringBuilder and StringBuffer are used for mutable string operations.
21. What is Serialization in java
Serialization in Java is the process of converting object data into a byte stream for storage or transmission over a network.
22. What is Regular Expression in java
Regular Expressions (regex) in Java are sequences of characters that define a search pattern, used for string matching and manipulation.
23. Collection in java
Collections in Java are containers that group multiple elements into a single unit, providing operations to manipulate and access them efficiently.
24. Difference between LinkedList and Set
LinkedList is a linear data structure where elements are stored in a sequential manner, while Set is a collection that does not allow duplicate elements.
25. Multithreading in java
Multithreading in Java allows concurrent execution of multiple threads within the same process, enabling efficient utilization of CPU resources.
26. What is Thread
A Thread in Java is a lightweight process that executes independently and shares resources with other threads within the same process.
27. What is MultiTasking in java
Multitasking in Java refers to the ability of a system to execute multiple tasks simultaneously, often achieved through multithreading.
28. Java 8 features
Java 8 introduced features like lambda expressions, functional interfaces, streams API, default methods in interfaces, and new Date/Time API.
29. Exception Handling in java
Exception Handling in Java manages runtime errors using try-catch blocks, finally block for cleanup, and throw keyword for custom exceptions.
30. 1/0 what exception in java
Dividing by zero in Java throws ArithmeticException, which indicates an error in arithmetic operations like division.
31. How to handle multiple exceptions
In Java, multiple exceptions are handled using multiple catch blocks or using a single catch block with '|' (pipe) separator to handle different exceptions.
32. Extends and implements
'extends' is used in Java for inheritance, where a subclass inherits properties and behaviors from a superclass, while 'implements' is used to implement interfaces, defining specific behaviors.
33. Marker Interface
A marker interface in Java has no methods or fields but is used to indicate specific capabilities or features to the JVM or other tools.
34. Difference between HashSet and LinkedList
HashSet is a collection that stores unique elements without any order, whereas LinkedList is an ordered collection where elements are stored in a sequence.
35. How many null values accept in list?
A List in Java can accept multiple null values, allowing null as a valid element.
36. What null values accepted in set?
A Set in Java typically does not accept duplicate elements, including null values, but some implementations like HashSet can accept a single null value.
37. Convert set to list?
To convert a Set to a List in Java, you can create a new ArrayList or LinkedList and pass the Set as an argument to the constructor.
38. Prime numbers? Code
Here's a code snippet to find prime numbers:
public List findPrimes(int[] arr) {
List primes = new ArrayList<>();
for (int num : arr) {
if (isPrime(num)) {
primes.add(num);
}
}
return primes;
}
private boolean isPrime(int num) {
if (num <= 1) {
return false;
}
for (int i = 2; i <= Math.sqrt(num); i++) {
if (num % i == 0) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
39. Input array [2,3,4,6,7,8,9,10,12,15,18]
Output array [2,3,5,7] Return array of elements which are actually prime
public List findPrimes(int[] arr) {
List primes = new ArrayList<>();
for (int num : arr) {
if (isPrime(num)) {
primes.add(num);
}
}
return primes;
}
private boolean isPrime(int num) {
if (num <= 1) {
return false;
}
for (int i = 2; i <= Math.sqrt(num); i++) {
if (num % i == 0) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
40. Difference between Comparable and Comparator?
Comparable is used to define the natural ordering of objects within a class, while Comparator allows for custom sorting logic to be applied to objects.
41. Difference between List and ArrayList?
List is an interface in Java that defines operations for ordered collections, while ArrayList is a class that implements List using a dynamically resizable array.
42. (“Dileep”,”Prasad”,”Yogesh”,”Bala” ) remove Yogesh from the list
To remove "Yogesh" from the list:
Listnames = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList("Dileep", "Prasad", "Yogesh", "Bala")); names.remove("Yogesh"); System.out.println(names); // Output: [Dileep, Prasad, Bala]
43. Sort Array using Java
To sort an array in Java, you can use Arrays.sort() method for primitive types or Collections.sort() for objects that implement Comparable or Comparator.
44. How to get last index of array in java
To get the last index of an array in Java:
int lastIndex = array.length - 1;
45. What is the super keyword in java?
The 'super' keyword in Java refers to the superclass of the current object instance, allowing access to superclass methods, constructors, and variables.
46. Can we define static method in Interface?
Yes, starting from Java 8, interfaces in Java can have static methods, which are associated with the interface itself rather than instances of the interface.
47. Difference between overloading and overriding?
Overloading refers to having multiple methods with the same name but different parameters within the same class, while overriding involves providing a new implementation for a method inherited from a superclass.
48. How to delete data from map?
To delete data from a Map in Java, you can use the remove() method by specifying the key of the element to be removed.
49. What is transaction in Java?
A transaction in Java refers to a sequence of operations treated as a single unit, ensuring atomicity, consistency, isolation, and durability (ACID properties) when manipulating data.
50. What are annotations in Java?
Annotations in Java provide metadata about a program, such as marking methods for compilation, runtime behaviors, or code generation instructions.
51. How to use @Autowired in spring boot application?
@Autowired in Spring Boot automatically injects dependencies into Spring-managed beans, reducing manual bean configuration and enhancing dependency injection capabilities.
52. How to filter employee on basis of salary?
To filter employees based on salary in Java:
ListReplace `Employee` with your actual class name and adjust the conditions as needed.filteredEmployees = employees.stream() .filter(e -> e.getSalary() > 10000) .collect(Collectors.toList());
53. Find all employee who are males and salary is greater than 10000 and age is greater than 20
To find employees meeting specific criteria like males with salary greater than 10000 and age greater than 20:
ListReplace `Employee` with your actual class name and adjust the conditions as needed.filteredEmployees = employees.stream() .filter(e -> e.getGender().equals("Male") && e.getSalary() > 10000 && e.getAge() > 20) .collect(Collectors.toList());
54. How to get property value of file?
To get a property value from a properties file in Java:
Properties prop = new Properties();
try (InputStream input = new FileInputStream("config.properties")) {
prop.load(input);
String value = prop.getProperty("property.key");
System.out.println(value); // Output the property value
} catch (IOException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
Replace `"config.properties"` with your actual properties file path and `"property.key"` with the key you want to retrieve.
55. Micro service?
A Microservice is a software architectural style that structures an application as a collection of loosely coupled services, each implementing a specific business capability.
Sure, here are the questions formatted with `` tags for answers in `
` tags, starting from serial number 56: 56. **What is the purpose of BeanFactory in Spring?**
BeanFactory in Spring is an interface for managing beans (objects) in an IoC (Inversion of Control) container, providing bean instantiation, dependency injection, lifecycle management, and bean configuration.
57. **What is the difference between ApplicationContext and BeanFactory in Spring?**ApplicationContext extends BeanFactory and provides additional functionalities like event propagation, internationalization support, and AOP integration, offering more extensive application context features in Spring.
58. **What is the use of the @Transactional annotation in Spring?**The @Transactional annotation in Spring manages database transactions, ensuring that a group of operations complete as a single unit of work, supporting rollback on failure and maintaining data integrity.
59. **Difference between JPA and Hibernate?**JPA is a specification for ORM frameworks in Java, while Hibernate is a popular ORM implementation, conforming to JPA standards but offering additional features like caching, inheritance mapping, and query optimization.
60. **How does Hibernate work in Java?**Hibernate is an ORM (Object-Relational Mapping) framework for Java, mapping Java classes to database tables and vice versa, providing query capabilities, caching, and transaction management for database operations.
61. **What is JPA?**Java Persistence API (JPA) is a specification for Java applications to manage relational data in databases, providing ORM (Object-Relational Mapping) capabilities for mapping Java objects to database tables.
62. **What is Swagger in Spring Boot?**Swagger in Spring Boot generates interactive API documentation from annotations in code, providing tools for API testing, client code generation, and maintaining consistency between API and documentation.
63. **How does AOP work in Spring?**Aspect-Oriented Programming (AOP) in Spring allows cross-cutting concerns like logging, security, and transaction management to be modularized and applied declaratively across multiple components using @Aspect and advice annotations.
64. **How to implement transactions in Spring Boot?**Implement transactions in Spring Boot using @Transactional annotation on service methods or classes, ensuring ACID properties (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability) for database operations.
65. **What is the difference between @RequestParam and @PathVariable?**@RequestParam in Spring MVC extracts query parameters from the request URL, while @PathVariable extracts values from URI templates (URL paths) mapped in @RequestMapping annotations.
66. **How to secure RESTful services in Spring Boot?**Secure RESTful services in Spring Boot using techniques like HTTPS, authentication (Basic, OAuth2, JWT), authorization (roles and permissions), and securing endpoints based on security requirements.
67. **What is Spring Data JPA?**Spring Data JPA is a part of the Spring Data project that simplifies data access through the JPA (Java Persistence API), providing repositories, query methods, and entity management for database operations.
68. **Difference between REST and SOAP?**REST (Representational State Transfer) is an architectural style using HTTP for communication, while SOAP (Simple Object Access Protocol) is a protocol for exchanging structured information using XML over various protocols.
69. **What are annotations in Spring?**Annotations in Spring like @Component, @Service, @Repository, @Autowired, @RestController, @RequestMapping, @Configuration, and @Bean are used for dependency injection, defining components, REST endpoints, and configuration.
70. **What is Spring Boot and its advantages?**Spring Boot is a framework for building production-ready Spring applications with minimal setup and configuration, offering advantages like auto-configuration, embedded servers, and dependency management.
71. **What is the use of the synchronized keyword?**The synchronized keyword in Java ensures thread safety by restricting concurrent access to shared resources or methods, preventing race conditions and data inconsistency in multithreaded environments.
72. **How does garbage collection work in Java?**Garbage Collection in Java automatically reclaims memory occupied by unreferenced objects, using algorithms like Mark and Sweep, Generational, and Concurrent to manage heap memory efficiently.
73. **How do you handle exceptions in Java?**Exceptions in Java are handled using try-catch blocks, finally block for cleanup actions, custom exception classes, and handling specific exceptions to ensure graceful error recovery and maintain application stability.
74. **What is the use of the finally block?**The finally block in Java ensures cleanup actions like closing resources (files, database connections) regardless of whether an exception occurs in the try block or not, ensuring reliable resource management.
75. **PreparedStatement and CallableStatement?**PreparedStatement in JDBC precompiles an SQL statement, improving performance and preventing SQL injection attacks, while CallableStatement executes stored procedures in the database, handling input and output parameters.
76. **JDBC connection?**JDBC (Java Database Connectivity) establishes a connection between Java applications and databases, using DriverManager or DataSource to execute SQL queries, retrieve data, and perform transactions.
77. **What is Spring Data?**Spring Data is a project in the Spring ecosystem that simplifies data access by providing abstractions and utilities for working with various data sources (relational databases, NoSQL databases, etc.) using Spring applications.
78. **What is the difference between stack and heap?**Stack in Java is used for method calls and local variables, managed in LIFO (Last In First Out) order, while heap is used for dynamic memory allocation of objects, managed by garbage collector.
79. **Memory allocation functions in Java?**Memory allocation in Java includes stack memory for method calls and local variables, heap memory for objects and instance variables, and method area for class-level data and code.
80. **Difference between HashMap and HashSet?**HashMap in Java stores key-value pairs, while HashSet stores unique elements, both using hashing to efficiently retrieve and store elements.
81. **What are collections?**Collections in Java are data structures that store and manipulate groups of objects, providing functionalities like insertion, deletion, traversal, and sorting.
82. **String reverse code?**To reverse a string in Java: ```java String str = "Hello"; String reversed = new StringBuilder(str).reverse().toString(); System.out.println(reversed); // Output: "olleH" ```
83. **What are the annotations you have used in Spring Boot?**Annotations used in Spring Boot include @SpringBootApplication, @RestController, @RequestMapping, @Autowired, @Service, @Component, @Repository, @Configuration, @Bean, and others for defining components, REST endpoints, and configuration.
84. **Explain basic Spring MVC architecture from starting to ending database?**Spring MVC architecture includes DispatcherServlet as front controller, HandlerMapping for mapping requests to appropriate handlers (controllers), Controller for processing requests, Model for data, and View for rendering responses, integrating with databases via Spring JDBC or Hibernate.
85. **What are OOP concepts in Java?**Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) concepts in Java include abstraction, encapsulation, inheritance, and polymorphism, promoting modular and reusable code.
86. **What is handler mapping?**HandlerMapping in Spring MVC maps incoming requests to appropriate handlers (controllers), based on URL patterns or request mappings defined in @RequestMapping annotations.
These should cover all the questions with their corresponding answers formatted as requested. Let me know if there's anything else you need!87. What is OAuth2 in microservices?
OAuth2 in microservices is an authorization framework enabling secure authentication and access control for client applications accessing protected resources, using tokens (access token, refresh token) and OAuth2 flows (Authorization Code, Implicit, Client Credentials).
88. What is Spring Data?
Spring Data is a part of the Spring Framework that simplifies data access and persistence in Java applications, providing repositories, query methods, and abstraction layers for interacting with relational databases (JPA), NoSQL databases, and cloud data services.
89. What is Spring Security?
Spring Security is a powerful authentication and authorization framework for securing Java applications, providing comprehensive security features like authentication (Basic, OAuth2, JWT), authorization (roles, permissions), and protection against common web vulnerabilities.
90. How to implement JWT authentication in Spring Boot?
Implement JWT authentication in Spring Boot using Spring Security, generating JWT tokens (access token, refresh token) for user authentication, validating tokens, and securing RESTful APIs based on user roles and permissions.
91. What is JPA in Spring Boot?
JPA (Java Persistence API) in Spring Boot is a standard specification for object-relational mapping (ORM) in Java applications, providing a set of APIs for managing relational data, entity mapping, and performing CRUD operations on databases.
92. How to implement CRUD operations in Spring Boot?
Implement CRUD operations in Spring Boot using Spring Data JPA repositories, defining entities, repository interfaces, and service classes to perform Create, Read, Update, and Delete operations on database entities, ensuring data persistence and retrieval.
93. What is Spring Batch?
Spring Batch is a framework for batch processing in Spring applications, providing reusable components (ItemReader, ItemProcessor, ItemWriter) for reading, processing, and writing large volumes of data efficiently, supporting batch jobs and ETL workflows.
94. What is Spring Integration?
Spring Integration is an extension of the Spring Framework for building enterprise integration solutions, supporting messaging patterns (message channels, endpoints), message transformation, and integration with external systems (JMS, FTP, HTTP).
95. How to implement messaging in Spring Boot?
Implement messaging in Spring Boot using Spring Integration or Spring Cloud Stream, configuring message channels, adapters (JMS, AMQP), and message listeners for asynchronous communication, event-driven architectures, and integrating with message brokers.
96. What is Spring WebFlux?
Spring WebFlux is a reactive web framework in Spring Boot for building non-blocking, asynchronous web applications, using Project Reactor (Mono, Flux) for handling concurrent requests, streaming data, and achieving high throughput and scalability.
97. How to handle concurrency in Spring Boot?
Handle concurrency in Spring Boot using synchronized methods, thread-safe components, asynchronous processing with CompletableFuture, or reactive programming with Spring WebFlux, ensuring safe and efficient execution of concurrent tasks and requests.
98. What is Spring Testing?
Spring Testing provides support for testing Spring applications and components using frameworks like JUnit, Mockito, and Spring's testing annotations (@SpringBootTest, @MockBean, @WebMvcTest), enabling unit testing, integration testing, and mocking dependencies.
99. How to implement validation in Spring Boot?
Implement validation in Spring Boot using Hibernate Validator with annotations (@NotNull, @Size, @Email) on entity fields, custom validation logic with Validator interface, and handling validation errors in controller methods for input data validation.
100. What is Spring Cloud Sleuth?
Spring Cloud Sleuth is a distributed tracing framework in Spring Boot for tracking and correlating microservices requests across distributed systems, generating unique trace IDs, spans, and integrating with Zipkin or ELK stack for performance monitoring.
101. What is Spring Boot Actuator?
Spring Boot Actuator is a feature in Spring Boot for monitoring and managing applications in production, providing endpoints (/health, /info, /metrics) for health checks, application insights, and exposing runtime metrics via HTTP or JMX.
102. What is Spring Boot Admin?
Spring Boot Admin is a web-based administration tool for managing and monitoring Spring Boot applications, providing an overview of application status, health metrics, configuration properties, and managing instances via a centralized dashboard.
103. What is Spring Cloud Config Server?
Spring Cloud Config Server is a centralized configuration management tool in microservices architecture, storing application configurations (properties, YAML files) in a version-controlled repository (Git, SVN), supporting dynamic updates and environment-specific settings.
104. What is Spring Cloud Netflix?
Spring Cloud Netflix is a set of libraries and tools in Spring Boot for building microservices on Netflix OSS components like Eureka (service discovery), Ribbon (client-side load balancing), Hystrix (circuit breaker), and Zuul (API gateway).
105. How to handle transactions in Spring Boot?
Handle transactions in Spring Boot using @Transactional annotation on service methods, enabling ACID properties (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability) for database operations, managing transaction boundaries and rollback scenarios.
106. What is Spring Boot CommandLineRunner?
Spring Boot CommandLineRunner is an interface for executing code at startup in Spring Boot applications, running tasks, initializing data, or performing setup operations before the application context is fully loaded and started.
107. What is Spring Boot ApplicationListener?
Spring Boot ApplicationListener is an interface for handling application events and lifecycle events (ContextStartedEvent, ContextStoppedEvent) in Spring Boot, registering listeners to react to events during application initialization, startup, or shutdown.
108. How to implement internationalization in Spring Boot?
Implement internationalization in Spring Boot using MessageSource for resolving localized messages (properties files), LocaleResolver for determining user's locale, and configuring locale change interceptor or @RequestMapping with locale parameter for multi-language support.
109. What is Spring Boot Data MongoDB?
Spring Boot Data MongoDB is an extension for MongoDB in Spring Boot applications, providing repositories, query methods, and abstraction layers (MongoTemplate) for interacting with MongoDB databases, performing CRUD operations and data access.
110. How to implement JWT authorization in Spring Boot?
Implement JWT authorization in Spring Boot using Spring Security, generating and validating JWT tokens (access token, refresh token), configuring JWT filters, and securing RESTful APIs based on user roles, permissions, and token validity.
111. What is Spring Boot Data Redis?
Spring Boot Data Redis is an extension for Redis in Spring Boot applications, providing repositories, RedisTemplate, and abstraction layers for interacting with Redis data structures (strings, hashes, lists), caching, and distributed data storage.
112. How to implement WebSocket in Spring Boot?
Implement WebSocket in Spring Boot using @ServerEndpoint (JSR-356) or WebSocketHandler (Spring WebSockets), handling bidirectional communication between clients and server over a persistent connection, supporting real-time messaging and event-driven architectures.
113. What is Spring Web MVC?
Spring Web MVC is a module in the Spring Framework for building web applications using Model-View-Controller architecture, providing components like DispatcherServlet, Controller, Model, ViewResolver, and supporting HTTP request handling, form submission, and rendering HTML responses.
114. What is Spring Boot Data JPA?
Spring Boot Data JPA is an extension for JPA (Java Persistence API) in Spring Boot applications, providing repositories, entity management, and abstraction layers for interacting with relational databases (MySQL, PostgreSQL), performing CRUD operations and data access.
115. How to implement batch processing in Spring Boot?
Implement batch processing in Spring Boot using Spring Batch framework, defining jobs, steps (ItemReader, ItemProcessor, ItemWriter), and job configurations (JobBuilderFactory, StepBuilderFactory) to process large volumes of data efficiently, supporting ETL workflows and batch jobs.
116. What is Spring Boot Thymeleaf?
Spring Boot Thymeleaf is a templating engine for web applications in Spring Boot, enabling server-side rendering of HTML templates with dynamic data, supporting expressions (Thymeleaf tags) for iterating lists, conditionals, and displaying data from Spring MVC models.
117. How to implement file download in Spring Boot?
Implement file download in Spring Boot using ResponseEntity with InputStreamResource or ByteArrayResource, configuring HTTP headers (Content-Disposition, Content-Type), and handling file downloads from local storage or external resources for serving files to clients.
118. What is Spring Boot Hibernate?
Spring Boot Hibernate integrates Hibernate ORM (Object-Relational Mapping) with Spring Boot applications, providing repositories, entity mappings, and abstraction layers for interacting with relational databases (MySQL, PostgreSQL), performing CRUD operations and data persistence.
119. How to implement logging in Spring Boot?
Implement logging in Spring Boot using SLF4J and Logback, configuring logging levels, appenders (ConsoleAppender, FileAppender), and log formats for capturing application events, debugging, and monitoring, integrating with centralized logging platforms (ELK stack, Splunk) for analytics.
120. What is Spring Boot DevTools?
Spring Boot DevTools is a development tool for improving developer productivity in Spring Boot applications, providing features like automatic application restart, live reload, embedded H2 console, and configuration properties refresh, enhancing development and testing workflows.
121. What is Spring Boot Security?
Spring Boot Security is a module for securing web applications in Spring Boot, providing authentication (Basic, Form, OAuth2, JWT) and authorization (roles, permissions), securing endpoints and resources, and protecting against common web vulnerabilities and attacks.
122. How to implement CORS in Spring Boot?
Implement CORS (Cross-Origin Resource Sharing) in Spring Boot using @CrossOrigin annotation, configuring CORS filter (CorsFilter), or global CORS configuration (WebMvcConfigurer), allowing cross-origin requests from specified origins, methods, and headers.
123. What is Spring Boot Test?
Spring Boot Test provides support for testing Spring applications using frameworks like JUnit, Mockito, and Spring's testing annotations (@SpringBootTest, @MockBean, @WebMvcTest), enabling unit testing, integration testing, mocking dependencies, and verifying application behavior.
124. How to implement async in Spring Boot?
Implement asynchronous processing in Spring Boot using @Async annotation with CompletableFuture or ListenableFuture, configuring ThreadPoolTaskExecutor for thread management, and handling concurrent tasks, improving application responsiveness and performance.
125. What is Spring Boot CommandLineRunner in Java?
Spring Boot CommandLineRunner is an interface for executing code at startup in Spring Boot applications, running tasks, initializing data, or performing setup operations before the application context is fully loaded and started.
126. How to send email in Spring Boot?
Send email in Spring Boot using JavaMailSender and MimeMessage, configuring SMTP properties (host, port, credentials), composing MimeMessage with email content (text, HTML, attachments), and sending emails programmatically from Spring Boot applications.
127. What is Spring Boot Data?
Spring Boot Data is an umbrella term for Spring Data projects in Spring Boot, providing support for data access and persistence with repositories, abstraction layers, and query methods for interacting with databases (JPA, MongoDB, Redis), NoSQL stores, and cloud data services.
128. How to implement pagination in Spring Boot?
Implement pagination in Spring Boot using Spring Data repositories (PagingAndSortingRepository), defining Pageable and Sort parameters in repository methods, and handling paginated data (Page, PageRequest) for retrieving and displaying large datasets in web applications.
129. What is Spring Boot Actuator in Java?
Spring Boot Actuator is a feature for monitoring and managing Spring Boot applications in production, providing HTTP endpoints (/health, /info, /metrics) for health checks, application insights, and exposing runtime metrics via HTTP or JMX for operational visibility.
130. How to implement logging in Spring Boot application?
Implement logging in Spring Boot using SLF4J and Logback, configuring logging levels, appenders (ConsoleAppender, FileAppender), and log formats for capturing application events, debugging, and monitoring, integrating with centralized logging platforms (ELK stack, Splunk) for analytics.
20 scenario-based questions and answers
1. Scalability and Performance:
How would you handle a significant increase in user transactions during peak hours in the banking application?
Answer:
Implementing auto-scaling based on metrics like CPU utilization, using caching mechanisms, and optimizing database queries would ensure the application scales effectively during peak loads.
2. Fault Tolerance and Resilience:
Describe a strategy to recover from a complete failure of a critical microservice in the banking application.
Answer:
Utilizing redundant instances of critical microservices across different availability zones, implementing automated failover mechanisms, and ensuring data replication and backup would facilitate recovery and minimize downtime.
3. Deployment Strategy:
How would you manage the deployment of microservices updates without affecting ongoing transactions in the banking application?
Answer:
Implementing zero-downtime deployment strategies such as rolling updates, canary releases, or blue-green deployments would ensure seamless updates while maintaining service availability.
4. Monitoring and Alerts:
Explain the importance of real-time monitoring and alerting in maintaining the performance and availability of the banking application.
Answer:
Real-time monitoring allows proactive detection of performance bottlenecks, resource utilization trends, and potential failures, enabling timely intervention and ensuring high availability.
5. Compliance and Security:
How would you ensure data security and compliance with regulatory standards like GDPR or PCI-DSS in the banking application?
Answer:
Implementing encryption for sensitive data, role-based access control (RBAC), regular security audits, and ensuring adherence to compliance standards through policy enforcement and monitoring would safeguard data and ensure regulatory compliance.
### Architecture Questions:6. Microservices Communication:
Compare the advantages of synchronous (RESTful APIs) versus asynchronous (message queues) communication between microservices in the banking application.
Answer:
Synchronous communication via RESTful APIs allows immediate responses and simplifies error handling, while asynchronous communication via message queues facilitates scalability, decoupling, and handling of high-volume transactions.
7. Database Design:
How would you design the database schema to handle concurrent transactions and ensure data consistency in the banking application?
Answer:
Using techniques like optimistic locking, database transactions, and ACID properties (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability) would ensure data integrity and consistency across concurrent transactions.
8. Event-Driven Architecture:
Explain how event-driven architecture would benefit real-time transaction processing in the banking application.
Answer:
Event-driven architecture enables immediate processing of transactions as events, facilitates decoupled communication between microservices, and supports scalability and responsiveness in real-time transaction processing.
9. Service Discovery and Load Balancing:
Discuss the role of service discovery and load balancing in achieving high availability and fault tolerance in the banking application.
Answer:
Service discovery enables dynamic registration and discovery of microservices, while load balancing distributes incoming requests across multiple instances, ensuring optimal resource utilization and resilience against service failures.
10. API Gateway:
How does an API gateway contribute to security, scalability, and management of APIs in the banking application?
Answer:
An API gateway provides centralized authentication, rate limiting, protocol translation, and API versioning, enhancing security, scalability, and simplifying API management across microservices.
### Development and Integration Questions:11. Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD):
Describe the CI/CD pipeline setup you would recommend for automating the deployment of microservices in the banking application.
Answer:
Implementing CI/CD pipelines with automated build, test, and deployment processes using tools like Jenkins or GitLab CI ensures rapid delivery of updates while maintaining quality and reliability.
12. Containerization and Orchestration:
How would you leverage Docker containers and Kubernetes orchestration for deploying and managing microservices in the banking application?
Answer:
Docker containers provide consistent runtime environments for microservices, while Kubernetes automates scaling, load balancing, and deployment management, ensuring efficiency, scalability, and resilience.
13. Data Consistency and Transaction Management:
Explain how you would ensure data consistency across distributed transactions in the banking application.
Answer:
Using distributed transaction management frameworks, employing compensation patterns for handling failures, and ensuring ACID compliance in database transactions would maintain data integrity across microservices.
14. Versioning and Compatibility:
Discuss the strategies you would employ to manage API versioning and ensure backward compatibility in the banking application.
Answer:
Implementing versioning through URI paths or headers, documenting changes, and using semantic versioning would facilitate seamless updates and backward compatibility without disrupting existing clients.
15. Performance Optimization:
How would you optimize the performance of database queries and ensure efficient data retrieval in the banking application?
Answer:
Utilizing indexing, query optimization techniques, database caching, and implementing data partitioning strategies would improve query performance, enhance scalability, and optimize data retrieval times.
16. Security Best Practices:
What are some best practices for securing APIs and preventing unauthorized access in the banking application?
Answer:
Implementing OAuth 2.0 for API authentication and authorization, enforcing HTTPS for secure communication, applying input validation and output encoding, and regular security assessments would mitigate security risks and safeguard sensitive data.
17. Resilient Design Patterns:
Discuss resilient design patterns like Circuit Breaker and Retry mechanisms and their relevance in the banking application.
Answer:
Circuit Breaker patterns prevent cascading failures by temporarily halting requests to a failing service, while Retry mechanisms automatically retry failed requests, improving fault tolerance and ensuring application resilience under varying conditions.
18. Logging and Monitoring:
How would you implement centralized logging and monitoring for microservices in the banking application?
Answer:
Using ELK stack (Elasticsearch, Logstash, Kibana) or similar tools for centralized logging, integrating with monitoring solutions like Prometheus or Grafana for real-time metrics, and setting up alerts would facilitate proactive monitoring and troubleshooting.
19. Cross-Functional Collaboration:
Explain the importance of cross-functional collaboration between development, operations, and security teams in ensuring the success of the banking project.
Answer:
Collaborative efforts foster shared responsibility, knowledge sharing, and faster resolution of issues, ensuring alignment with business goals, adherence to standards, and continuous improvement in application quality and performance.
20. Scaling Strategies:
How would you plan for horizontal scaling of microservices in response to growing demand in the banking application?
Answer:
Implementing container orchestration platforms like Kubernetes for automatic scaling, utilizing cloud provider scaling services based on metrics, and optimizing microservices architecture for elasticity would facilitate seamless horizontal scaling and meet increasing demands effectively.