java8 Interview Quesions
1.could you please provide an introduction about yourself? & Explain about your current project Details and roles & responsibilities? video available
Hi, good morning Satish! My name is Sreenu, I am from Telangana. I have over 7 years of experience in the IT industry. Currently, I am employed at Persistence System. my current project name is SG Wealth, I've been involved in that I Developed User Registration Module within the banking domain.
For that implementation, we are using the technologies such as Java, Spring, Spring Boot, Microservices, Spring Security, Spring Data JPA,and a MySQL database for the backend. and frontend side we are using HTML, CSS, Bootstrap, JavaScript, jQuery, and Angular.
These technologies used to developed the application.
and my Roles and Responsibilities:
1) Read FDD (Functinalies Design Document) and understand the Requirement
2) If I have any questions in requirement, notedown and ask to functional team in daily meeting
3) Design Database tables
4) Prepare insert queries to insert data in static table
5) Analyze components(classes and methods)
6) Create project for backend, and implement code for backend(Rest API)
7) Test the Backend API Using Swagger UI/POSTMAN
8) Write a JUNIT Test cases for every indiudual API's
9) Maintain the code coverage minimum 95%
10) then push the code into Gitrepository
11) Deploy the backend application in AWS cloud by using help of Jenkin Tool
11) Deploy the backend application in AWS cloud by using help of Jenkin Tool
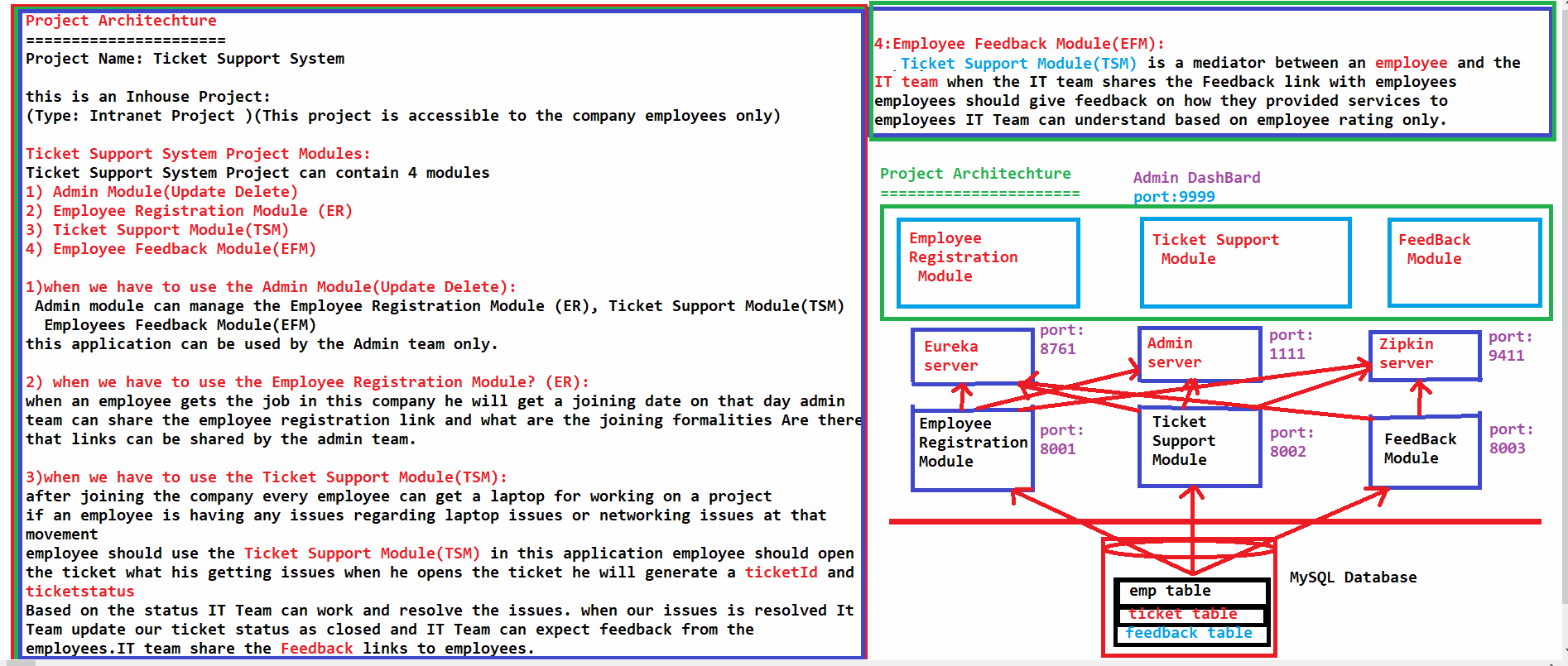
2. Explain about your current project Architechture & request,response flow? video available
Java8 Features
-> java1.8 introduced lot of features
-> java1.8 new features changed java programing style
Main Objectives of java 1.8 vereion
-> simplify java programming
-> Enable functional progaming
-> Write more readable and consice code
What are the Java 1.8 Features
1) Interface changes
1.1) default method
1.2) static method
2) Functinal Interfaces (@FunctionalInterface)
2.1 Predicate & BiPredicate====>test() method
we can use Predicate Interface if we want to check condition then we can use predicate functional interface.
2.2 Function & BiFunction======>apply() method
2.3 Consumer & BiConsumer ===> accept() method
2.4 Supplier ===> get() method
3) Lambda Expression
4) Method Refference & Constructor Reference
5) Stream API
6) Optional class(to avoid null pointer Exception)
7) spliteterator
8) StringJoiner
9) forEach() method
10) Date & Time API
what is Interface Changes?
-> interface means collection of abstract methods
->Note: The method which doesn't content method body is called abastract method
-> A class implement interface using "implements"
-> when a class is implementing interface its mandatory that class should implement all abstract method of that interface other wise that class con't be compile
Example:
// Interface representing a general Vehicle
interface Vehicle {
// Method to start the engine
void startEngine();
}
// Class implementing Vehicle interface
class Car implements Vehicle {
// Implementing method from Vehicle interface
public void startEngine() {
System.out.println("Car engine is starting");
}
}
// Class implementing Vehicle interface
class HybridCar implements Vehicle {
// Implementing method from Vehicle interface
public void startEngine() {
System.out.println("HybridCar engine is starting");
}
}
Note: if we add new abstract method in interface "Vehicle" then Car class, HybridCar class will fail at compile time
To over come this problem we will use static & default methods
1)interface can have concrete methods from 1.8 version
2) interface concreate method shoud be defalut or static
3) interface default method we can override in implementation classes
4) interface static method we con't override in implementation classes
5) we can write multiple default or static method in interface
6) default or static method introduce to provide backward compatability
Example:
forEach() method added in java.util.Itarable interface as derault method in 1.8 version
package com.soft.opp2;
interface Vehicle {
void m1();
public default void m2(){
System.out.println("this is default method inside interface");
}
public static void m3() {
System.out.println("this is static method in inside interface");
}
}
class Car implements Vehicle{
@Override
public void m1() {
System.out.println("implemented method");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Car c=new Car();
c.m1();
Vehicle.m3();
}
}
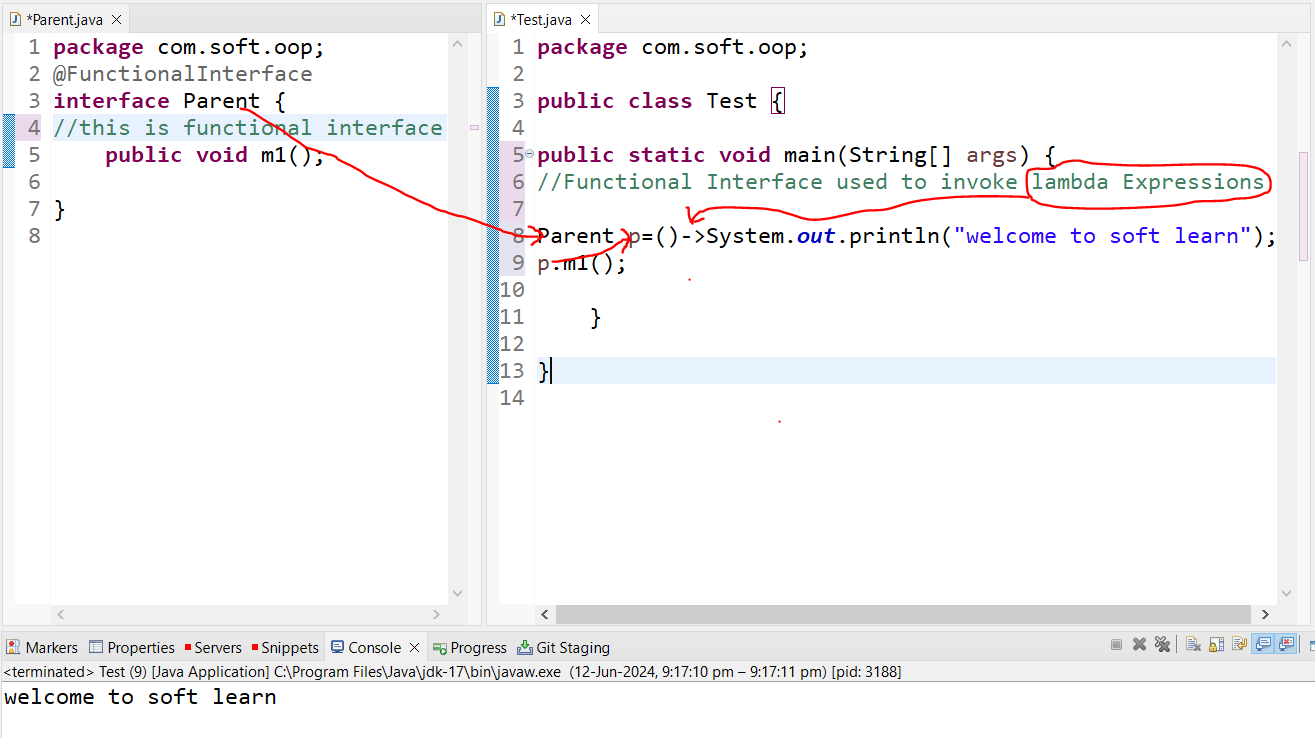
Lambda Expression
-> Lambda Expression introduce in java1.8 version
-> Java is called as Object Orinted Programing language everything will be represented using class and Objects.
-> From java 1.8 onwards java is also called as Functional Programing Languages
-> In OOP Languages classes, objects are main Entities we need to write methods in side the class only.
-> Functional Programing means everything will be represented in the form of Functions. Functions can exits out side of the class Functon can be stored into a reference variable. A Function can be passed as parameter to others methods.
-> Lambda Expression introduced in java to enable Functional Programing
what is Lambda Expression
Lambda is an Anonymous function
-->No MethodName
--> No Modifier
--> No Return Type
Example 1: Create Normal Method
public void m1() {
System.out.println("implemented method");
}
============================Example 1: Create Lambda
()-> System.out.println("implemented method");
Example 2: Create Normal Method
public void add(int a, int b) {
System.out.println(a+b);
}
============================Example 2: Create Lambda
(a,b)-> System.out.println(a+b);
Example 3: Create Lambda
(a,b)->{ return a+b;}
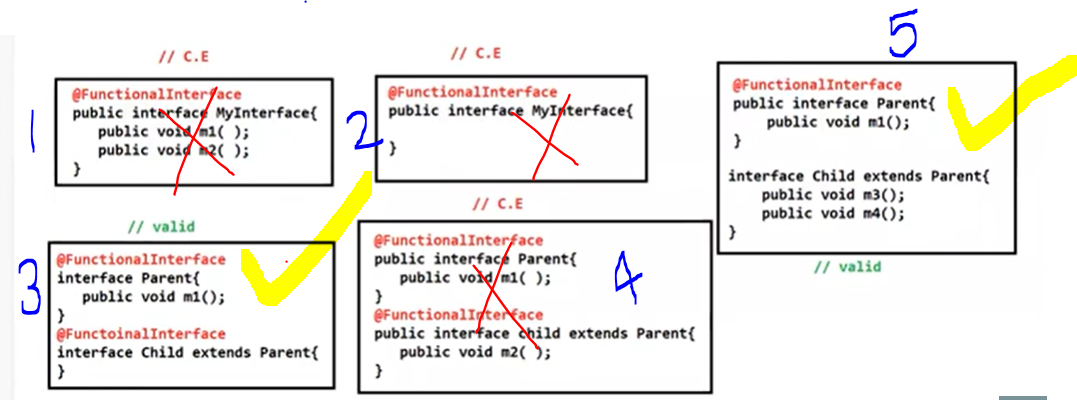
Functional Interface:
1) The Functional Interface can contains only one abastract method is called Functional interface
2) Functional Interface used to invoke lambda Expressions
3) Below are given Functional Interfaces
Runnable=====> run() method
Callable=====> call() method
Comparable===> campareTo() method
*** To represent one interface as a functional Interface then we can use @FunctionalInterface annotation
Example:
@FunctionalInterface
public interface MyInterface{
public void m1();
}
Identify the Functional Interface Tricky Interview quations:
How to call functional interface using lambda Expression Example:
@FunctionalInterface annotation :
when we use @FunctionalInterface annotation our compiler will check interface can contains only one abstract method or not
in java8 there are multiple predefined functional interface introduced
1. Predicate, ===>takes input==> returns true or false ==> test() method ==>(PT)
2. Function, ===>will take input ==> will return output ==>apply() method==>(FA)
3. Consumer, ==> will take input ==>will not return anything ==>accept() method==>(CA)
4. Suplier, ==> will not take any input ==> return output get() method==> (SG)
The above Functional Interface are provided in java.util.function package
1. Predicate ===>takes input==> returns true or false ==> test() method
==> it is predifiend functional interface
==> it is used to condition and returns boolean value true or false
==> predicate interface having only one abstract method that is test() method
Example:
interface Predicate{
boolean test(T t);
}
Predicate Example Program:
import java.util.function.Predicate;
public class PredicateExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Predicate p=i-> i> 10;
System.out.println(p.test(5));
}
}
POC'S declare names in arrays and print which name start with 'S'
import java.util.function.Predicate;
public class PredicateExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] names= {"Sreenu","Akil","Ramesh","Balu","Srikanth","Susmitha"};
Predicate p= name-> name.charAt(0)=='S';
for(String name:names) {
if(p.test(name)) {
System.out.println(name);
}
}
}
}
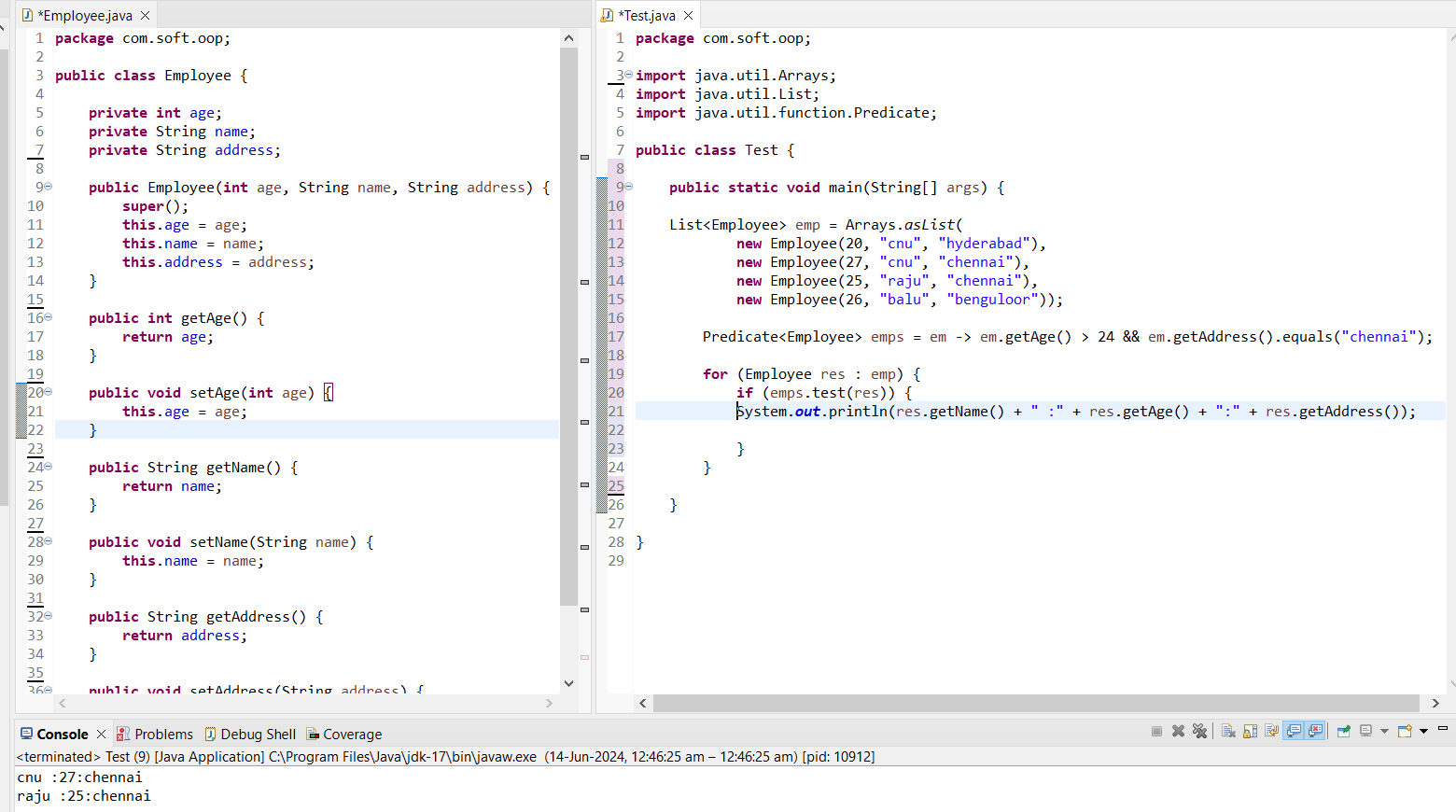
2nd Task: print greterthen 23 age persoin details
package com.soft.operators;
public class Person {
private String name;
private Integer age;
public Person(String name, Integer age) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
================================================
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.function.Predicate;
public class PredicateExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List persons = Arrays.asList(new Person("shiva", 20), new Person("shiva", 23), new Person("raja", 25),
new Person("bharath", 27));
Predicate p = age -> age > 23;
for (Person person : persons) {
if (p.test(person.getAge())) {
System.out.println(person.getName() + " " + person.getAge());
}
}
}
}
output:
raja 25
bharath 27
2. Function Functional Interface ===>will not take any input ==>return output ==>apply() method
=> Function is a predefined Functional interface
=> Function Interface having one abstract method apply() method
interface Function{
R apply(T t);
}
==>It take input and returns output
Example 1:
import java.util.function.Function;
public class FunctionExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Function f= (name)->name.length();
System.out.println(f.apply("Sreenu"));
System.out.println(f.apply("Nenavath"));
System.out.println(f.apply("Softlearn"));
}
}
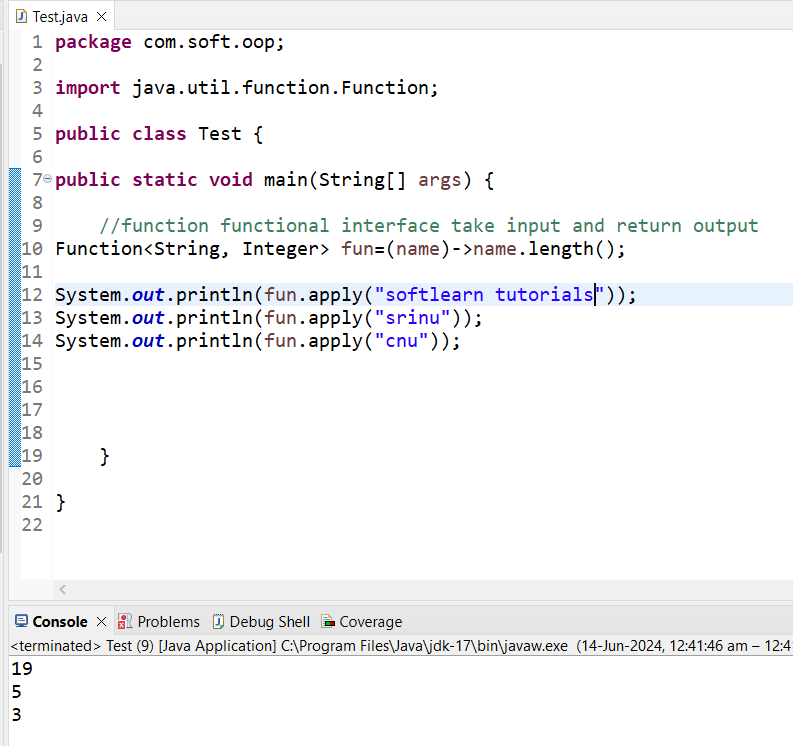
Task2: Take two inputs and perform sum of two input and return output
import java.util.function.BiFunction;
public class BiFunctionExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BiFunction bif= (a,b)->a+b;
System.out.println(bif.apply(10, 20));
}
}
3. Consumer
Consumer, ==> will take input ==>will not return anything ==>accept() method==>(CA)
=> Consumer is a predefined Functional interface
=> Consumer Interface having one abstract method accept() method
=> Consumer will accept input but it won't return anything.
=> Note: forEach() method internally use consumer only
Example Program:
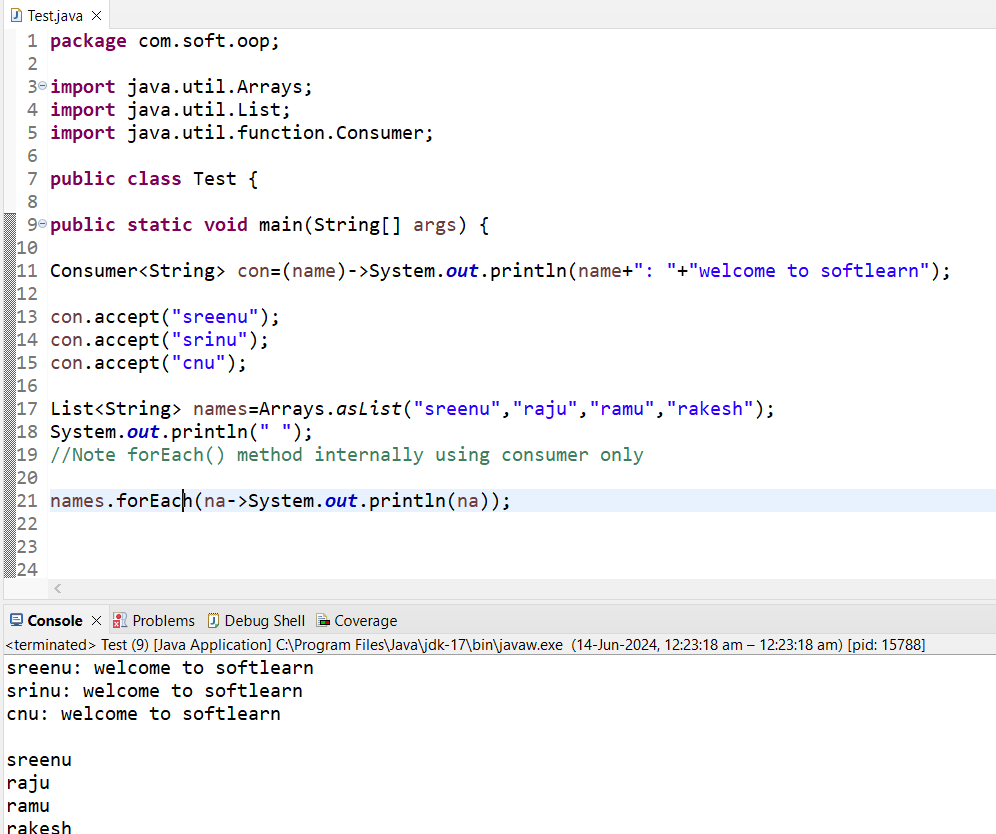
4. Suplier
Suplier, ==> will not take any input ==> return output get() method==> (SG)
=> Suplier is a predefined Functional interface
=> Suplier Interface having one abstract method get() method
=> Suplier will accept input and it return output.
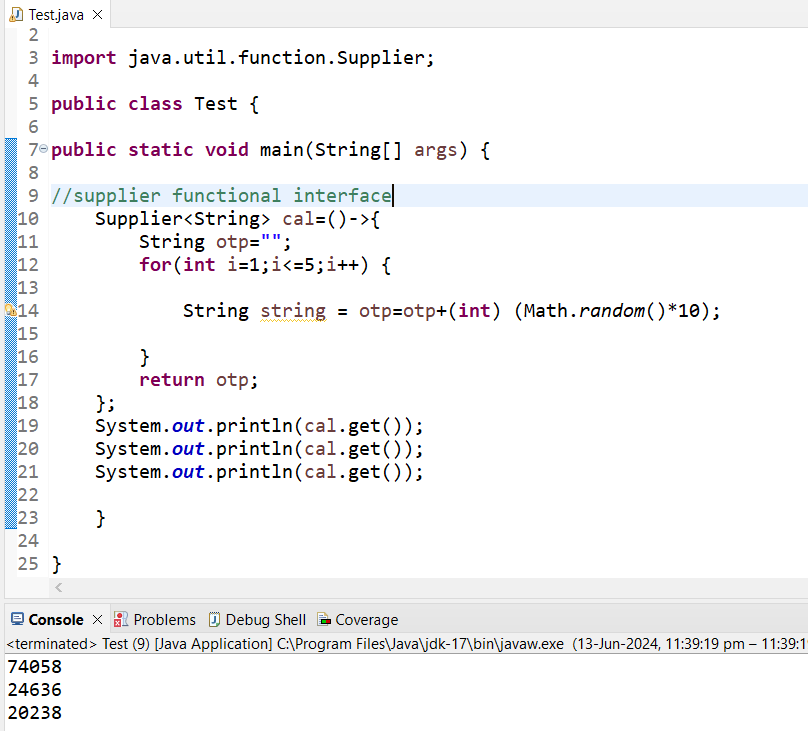
Method Refferences:
Method Refferences means refference to the method
Constructor Refference means reffrence to the constructors
StringJoiners
forEach() method
Optional Class:
Stream ApI
Stream ApIStream Api introduced in java8 version
Streams represent a sequence of elements and support various operations to perform computations on these elements either sequentially or in parallel.
They don't store data; they provide a way to interact with collections (or other data sources) in a declarative way.
Note: Collections are used to store the data
Stream Creation:
===========
we can create stream in two ways
1) stream.of(element1, element1, element1,element1.....)
2) stream() method
Example:
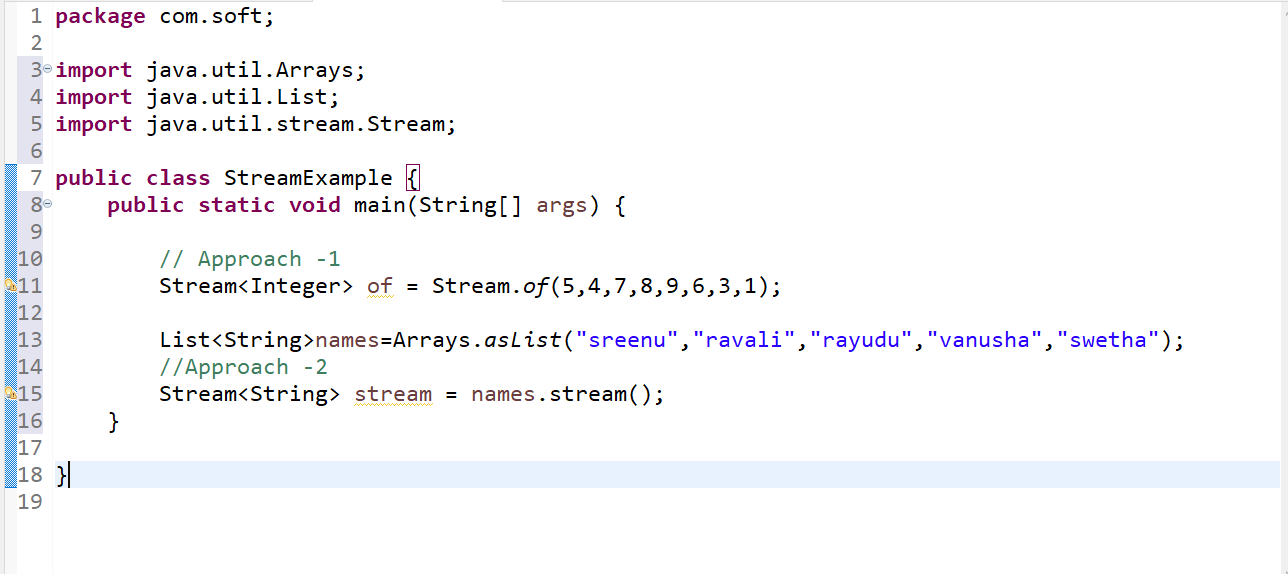
Stream Operations:
===============
==> stream API provide several methods to perform operation on the data.
we can devide stream API methods in 2 types
1) Intermediate Operation
2) Terminal Operation
1) Intermediate Operation
================
Interview Quations
1) Print all Even Numbers from given list by using stream Functions?video will come soon
2) print all Duplicate Numbers from given list using stream Function? video will come soon
3) print all Duplicate Numbers count from given list using stream Function? video will come soon
4) print all Duplicate character count from given string using stream Function? video will come soon
5) print non repeated character from given string using stream Function ?video will come soon
6) print all the numbers starting with 1 form given list using stream funciotns? video will come soon
7) print first element from the given list using stream functions? video will come soon
8) print total numbers from the given list using stream functions? video will come soon
9) pring Max value fromt the given list using stream funtions? video will come soon
10) print given element ascending order using stream funciotns or print given element sorting order using stream funciotns? video will come soon
11) print given element Descendign order using stream funciotns ?video will come soon
12) pring vowels from the given String using stream funcctions? video will come soon
with out using java8 stram function
13) Print all Even Numbers from given list without using stream Functions?video will come soon
14) print all Duplicate Numbers from given list without using stream Function? video will come soon
15) print all Duplicate Numbers count from given list without using stream Function? video will come soon
16) print all Duplicate character count from given string without using stream Function? video will come soon
17) print non repeated character from given string without using stream Function ?video will come soon
18) print all the numbers starting with 1 form given list without using stream funciotns? video will come soon
19) print first element from the given list without using stream functions? video will come soon
20) print total numbers from the given list without using stream functions? video will come soon
21) pring Max value fromt the given list without using stream funtions? video will come soon
22) print given element ascending order without using stream funciotns or print given element sorting order using stream funciotns? video will come soon
23) print given element Descendign order without using stream funciotns ?video will come soon
24) pring vowels from the given String without using stream funcctions? video will come soon